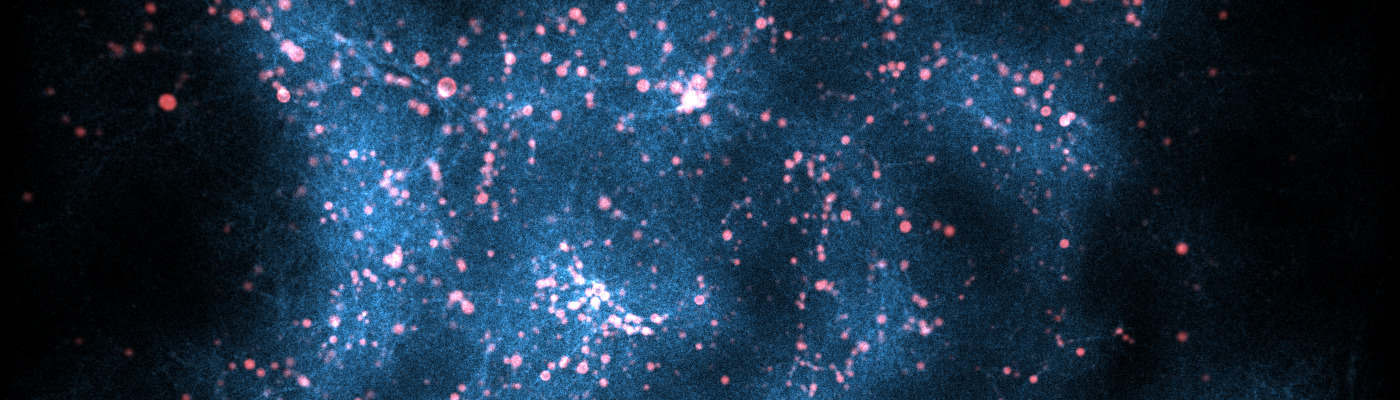
 Visualization of LAEs on cosmological scales: Observed intensity (blue) and star forming regions in galaxies (red).
Visualization of LAEs on cosmological scales: Observed intensity (blue) and star forming regions in galaxies (red).
Cosmological radiative transfer simulations of Lyman-alpha emission: the impact on the galaxy clustering
Abstract
Lyman-alpha emitters and their intensity map are powerful probes of the large-scale structure at optical and near-infrared wavelength as HETDEX plans. However, the fact that the Lyman-alpha photons are scattered due to the neutral hydrogen has non-negligible impact on the observed distribution of Lyman-alpha photons. To study this in detail, we run a suit of radiative transfer (RT) simulations on Illustris and quantify the impact of RT on the real space galaxy clustering (Behrens, CB et al. arXiv: 1710.06171).
Date
Feb 5, 2018 6:10 PM — 6:25 PM
Location
Aspen, United States