The impact of Lyman-α radiative transfer on large-scale clustering in the Illustris simulation
Abstract
Lyman-$\alpha$ emitters (LAEs) are a promising probe of the large-scale structure at high redshift, $z\gtrsim 2$. In particular, the Hobby-Eberly Telescope Dark Energy Experiment aims at observing LAEs at 1.9 $<z<$ 3.5 to measure the Baryon Acoustic Oscillation (BAO) scale and the Redshift-Space Distortion (RSD). However, (Zheng et al. 2011) pointed out that the complicated radiative transfer (RT) of the resonant Lyman-$\alpha$ emission line generates an anisotropic selection bias in the LAE clustering on large scales, $s\gtrsim 10,{\rm Mpc}$. This effect could potentially induce a systematic error in the BAO and RSD measurements. Also, (Croft et al. 2016) claims an observational evidence of the effect in the Lyman-$\alpha$ intensity map, albeit statistically insignificant. We aim at quantifying the impact of the Lyman-$\alpha$ RT on the large-scale galaxy clustering in detail. For this purpose, we study the correlations between the large-scale environment and the ratio of an apparent Lyman-$\alpha$ luminosity to an intrinsic one, which we call the “observed fraction”, at $2<z<6$. We apply our Lyman-$\alpha$ RT code by post-processing the full Illustris simulations. We simply assume that the intrinsic luminosity of the Lyman-$\alpha$ emission is proportional to the star formation rate of galaxies in Illustris, yielding a sufficiently large sample of LAEs to measure the anisotropic selection bias. We find little correlations between large-scale environment and the observed fraction induced by the RT, and hence a smaller anisotropic selection bias than what was claimed by (Zheng et al. 2011). We argue that the anisotropy was overestimated in the previous work due to the insufficient spatial resolution: it is important to keep the resolution such that it resolves the high density region down to the scale of the interstellar medium, $\sim1$ physical kpc. We also find that the correlation can be further enhanced by assumptions in modeling intrinsic Lyman-$\alpha$ emission.
Motivation
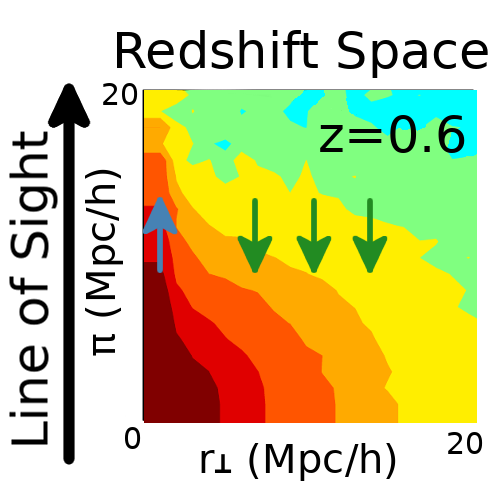
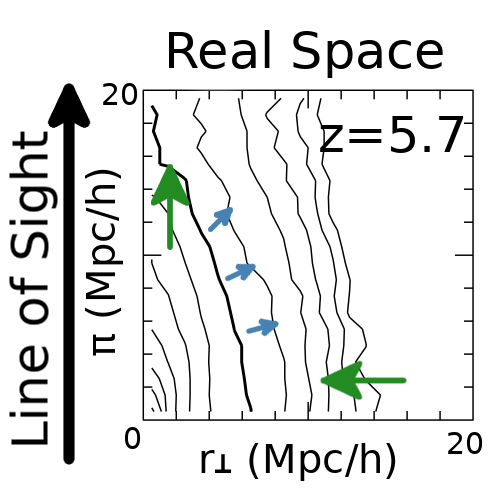
Summary
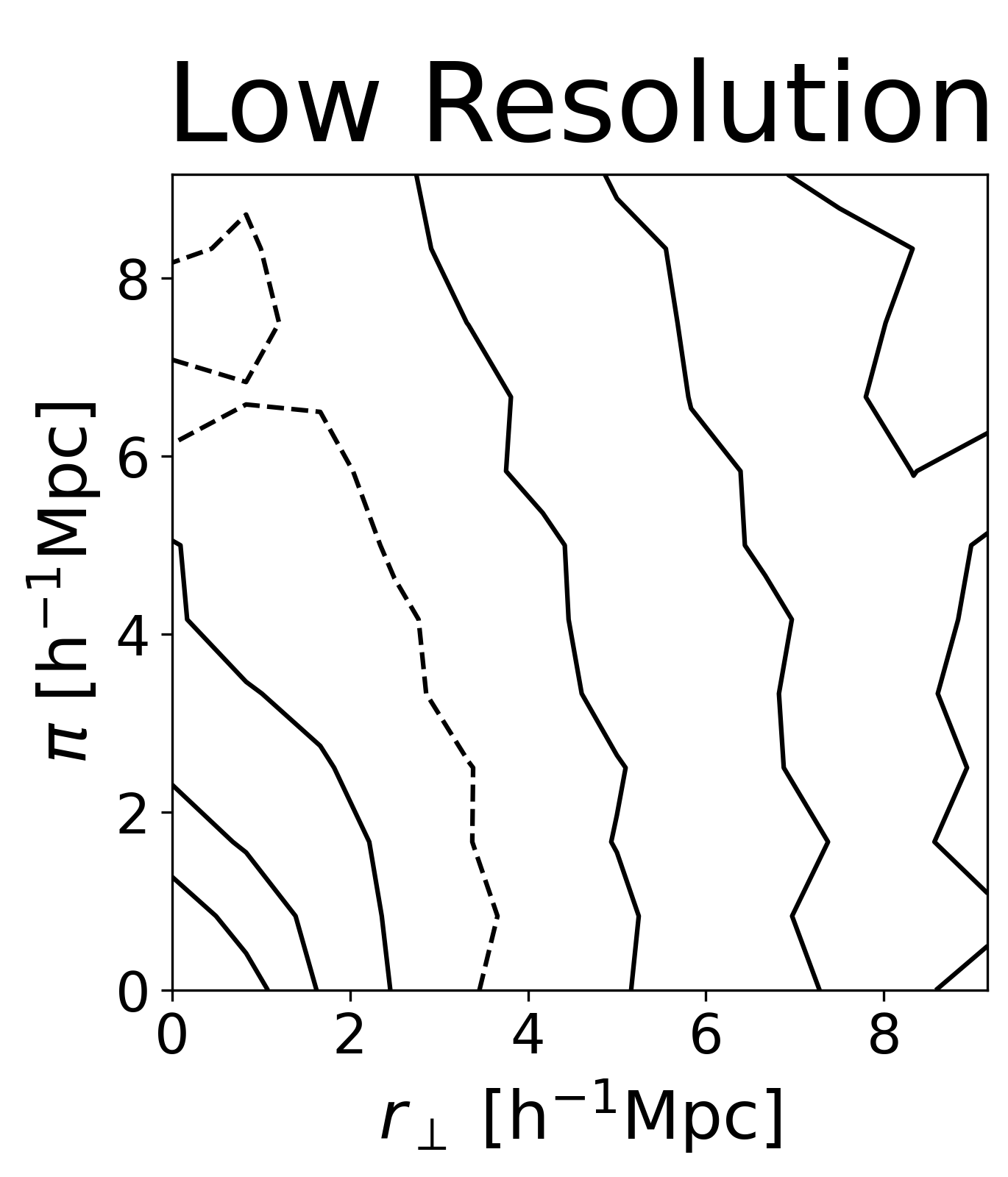
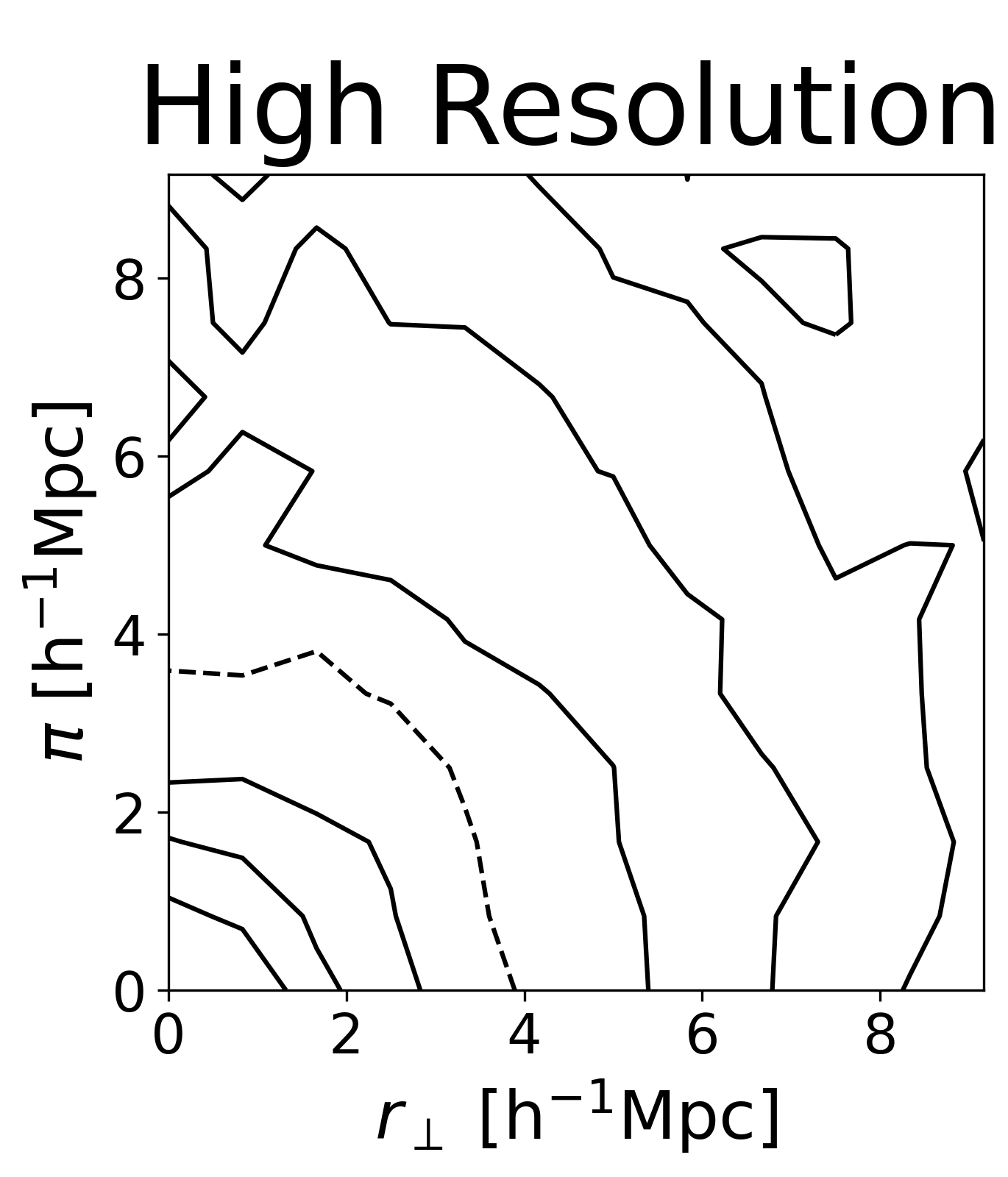
While we demonstrated in this paper that there is no radiative transfer distortion effect in our simulations, this does not exclude the possible existence of such effect in reality: The effect strongly depends on the spectrum on leaving the CGM. Dust and clumpiness might strongly effect this spectrum and thus the strength of a possible distortion effect. Future improvements in understanding in the multi-scale modeling (ISM/CGM/IGM) of Lyman-$\alpha$ emitter observations will help settling this question.